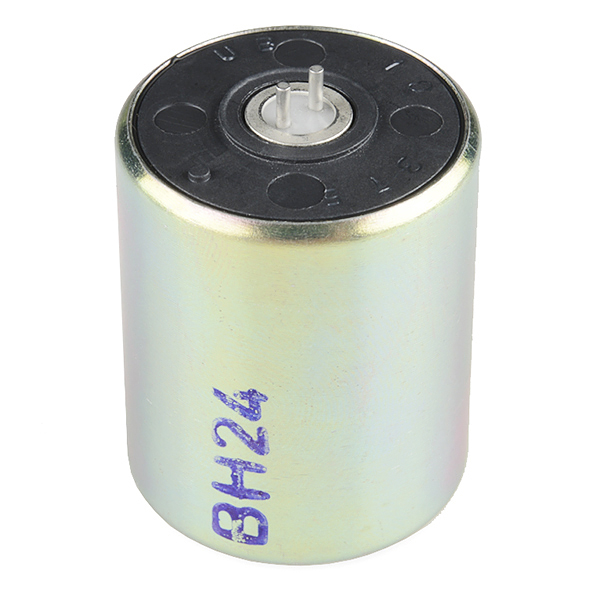
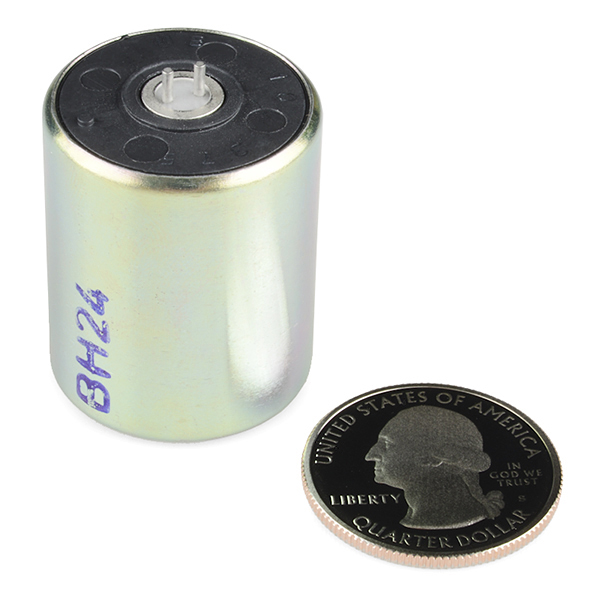
Geophone - SM-24, with Insulating Disc
Need to put your finger on the pulse of the Earth? Did I just blow your mind? A geophone works by translating ground movement into voltage, which can easily be read by a microcontroller. The SM-24 geophone element is designed to offer the highest performance in seismic exploration based upon field-proven I/O Sensor technology. Low distortion, combined with excellent specifications, provide high-fidelity data. Basically, it's a super low frequency microphone for the ground.
Perfect for all of your 2-D & 3-D seismic exploration needs with bandwidth from 10 Hz up to 240 Hz
This is an upright basic unit with insulating disc.
- Tight specification, low-distortion vertical geophone
- Extended spurious over 240 Hz, allowing full bandwidth at 2-ms sampling
- Sensitivity of 28.8 V/m/s
- Upright Basic Unit with Insulating Disc
Geophone - SM-24, with Insulating Disc Product Help and Resources
7 of 7 found this helpful:
Polarity
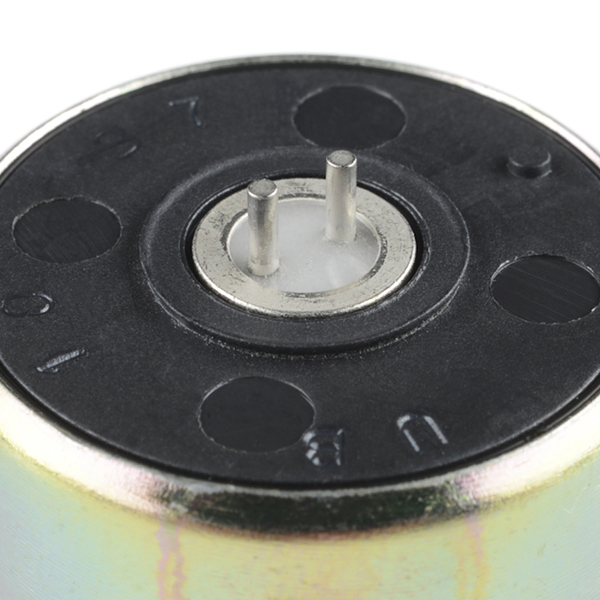
An engineer from ION (the company that manufacturer's the SM-24) indicated that there is a polarity to the geophone. The pin that is closest to the notch is the geophone's positive terminal. With two or more geophones in a project, you will need to make sure that the sensors are wired in the same orientation. Otherwise, the signals will cancel each other out.
2 of 2 found this helpful:
Going Further: Additional Tutorials and Examples
Core Skill: Electrical Prototyping
If it requires power, you need to know how much, what all the pins do, and how to hook it up. You may need to reference datasheets, schematics, and know the ins and outs of electronics.
Skill Level: Noob - You don't need to reference a datasheet, but you will need to know basic power requirements.
See all skill levels
Comments
Looking for answers to technical questions?
We welcome your comments and suggestions below. However, if you are looking for solutions to technical questions please see our Technical Assistance page.
Customer Reviews
4.3 out of 5
Based on 3 ratings:
5 of 5 found this helpful:
A bargain!
Sure, it's not a calibrated geophone, but it does the job for us. We use it in the optics lab to hunt down the sources of vibrations. Feed it into a dynamic signal analyzer, oscilloscope, or data acquisition system and you're good to go. Remember to add the specified damping resistor across the geophone's outputs.
Thank you!
Received on time and working as expected. Thank you.





1) One of tutorial links shows a resistor on the geophone. What is it for? Do I need it? If so, what is the resistance required? https://create.arduino.cc/projecthub/team-protocentral/measuring-seismic-activity-using-protocentral-openpressure-702324 2) I purchased the ADS1220 amplifier used in that link and wired it up. Although the signal increases if I shake it, it has this weird look to it, it seems squarish, with lots of 0 values. Anyone know what could be the issue? https://i.imgur.com/hNdHcuM.png 3) The ADC seems to saturate when pick up and shake the geophone gently. Is this normal? Anyone know what could be causing this? 4) Is there a recommended amplifier/ADC I can buy to get a reasonable looking signal?
For technical assistance please follow the link at the top of the comment section, above the comment submission area.
There is a markup error in the documents section with the datasheet link which currently reads: [Datasheet](http://cdn.sparkfun.com/datasheets/Sensors/Accelerometers/SM-24 Brochure.pdf)
Thanks, some changes on our backend broke a bunch of links and we are slowly finding them. It is all fixed.
For the inductor in the amplifier circuit in the example code, would any coil work? Thanks.
how to interface a geophone with arduino uno directly ?? kindly help me
Use these to set up a perimeter around your house and detect intruders!
Quote from above "A geophone works by translating ground movement into voltage, which can easily be read by a microcontroller"
Please SF provide a schematic "application circuit" to interface your Geophone to an Arduino! It is not that simple to hookup to the Arduino A/D input. You probably need a precision OPA (24 bit) and some low pass cut off filters.
http://arduino.cc/forum/index.php?topic=73149.0
A good start for a geophone analog amplifier circuit is here. It's very low power and highly sensitive. It'd be nice if somebody made a Seismic Shield product based on this circuit (wink wink nudge nudge).
A simple geophone display, commonly used in ghost hunting equipment, is here. But it's not very sensitive and doesn't have an analog output.
An example project that works well with the SM-24 sensor and has an analog output option is here.
A lower cost (surplus) sensor that's almost exactly the same size, but is a little less sensitive, can be found here.
I'm currently working on hooking the geophone up to an Arduino. I've constructed an amplifier shield that seems to work (as in "my oscilloscope displays waveforms" and "a pin drop is easily detected on a wooden table"), and I have working Arduino code that reads samples from an analog input and makes an appropriate frequency analysis. So, barring any wildly unforeseen problems the entire setup might actually work already.
The memory use for the frequency analysis requires an Arduino Mega or an Arduino Due. I have a Due but unfortunately the amplifier requires at least 5V, causing its output to be dangerous to the Due's analog inputs, so I'll have to wait until I've received a Mega.
If I get it to work, I'll upload the entire thing to Github and keep you posted in these comments.
Edit: the prototype is already working and runs on a UDOO board meaning it should work on an Arduino Due. Find schematics, board, and code here: https://github.com/olewolf/geophone.
I've been trying to follow your example from your video on youtube and the github schematic, though it seems like the schematic is different than the video? I can't seem to get the amp circuits right, always getting a steady value output. I'm new to this so I must be doing it wrong! :) The best results I have gotten so far is to put the one geophone connection on 3.5v and the other to the Arduino Analog input. But am I losing out on accuracy this way?
I'm not sure if you're asking me, but I haven't made a video so that may be the reason you're seeing a difference. :)
Sure, you can hook it up directly if you want. It will work.
What you suggest about precision op amps and an LPF is exactly how high-end seismic equipment is created.
Found another datasheet with readable graphs: SM-24
I know this is just copied from the datasheet, but "Extended spurious over 240 Hz..."? Maybe "Extended spurious frequency rejection over 240 Hz..."?
Could the geophone be combined with this or this to create a through-earth communication system? Does anyone know the sound velocity characteristics of concrete or limestone?
I'm having a bit of trouble reconciling the "bandwidth" (frequency response?) spec on this thing with the chart in the data sheet, which seems to show a pretty flat response from around 50 Hz through 1 kHz. I can see why you'd need a pretty good LPF between this thing and an A/D converter with a 500 Hz sampling rate.
Before I spend $59 on a Geophone sensor, I would like to see a Sparkfun application circuit that will work with the Arduino!
I see that this sensor has a sensitivity from 10 to 240Hz... so could this be used to detect and record infrasound? I was looking at several electret microphones but I could not found one that had a sensitivity below 20Hz.
The datasheet on this thing is pretty weak compared to some of the other products. For most of the accelerometers there is code and detailed instructions on how to hook it up. Can anyone point me to a walk through of how to connect this thing to an arduino?
Quote "Sure, you can hook it up directly if you want. It will work."
I may have been a little too quick to type that.
Since the arduino doesn't have differential inputs, you'd have to inject a voltage 1/2 of your ADC reference voltage.
I'd like to see a schematic too. I do have a few of my own personal schematics to interface these types of sensors to ADCs. Can I give my email address on here?
I don't see why you couldn't but remember, once it's out there it is OUT there.
I agree and apologize for any possible disinformation. You can however hook these up directly to any ADC with differential inputs.
You could always use a photo sharing site and post the links.
Interesting, but I'd also like to see you offer an good quality (but really cheap!!) infrasound detector - i.e. down to around 0.02Hz.
I think those are better built than sourced, but suggest one and prove me wrong! Google for amateur seismographs and you'll come up with some interesting designs.
Yeah, I've seen the amateur ones - trouble is I don't have much skill at building. But as I can't find a commercial one either (I hoped you might have come across one on your travels), it looks like I'll have to build one. And then figure out how on earth to calibrate it.....
I see what you did there "How on Earth". haha good one.
Perfect for keeping tabs on the mole men.
Tell you how old I am. Those little guys with that awesome ray gun (vacuum cleaner and a funnel) scared the daylights outta me! I was plenty glad when Superman got them back down that well! Makes me wonder, why did Hollywood decide you need $100 million special effects in kids films.
Overkill contact microphone?
Actually, according to the (incredibly low resolution) pictures on the datasheet. This appears to be a dynamic microphone. I wonder how well it would operate as a low frequency speaker?
It is a good quality magnet suspended by springs, surrounded by a coil. So, very similar to a microphone. Also these are similar to an accelerometer as well, just made for lower frequencies. I work with these all the time at my job.
All you need to know is a few things to get started:
Orientation... there are vertical and horizontal orientated versions which allow you to create a true tri-axial configuration using 3 geophones (1 vertical, 2 horizontal).
Sensitivity. Volt/inch per sec.
Frequency response. Most geophones are very linear from about 2-500hz. There will be a higher sensitivity in the geo's sweet spot or natural frequency. You can also use a dampening resistor to make it much more linear in response but at the cost of sensitivity.
Cool, thanks for the info. I've seen some super powerful surface transducers with similar designs (except they had 2 symmetrical magnets, and a pair of voice coils). This would probably work great for recording explosions. Low frequencies travel right along the ground, so burying it shallow, or embedding it in something heavy on the ground would probably work well. I may have to look into getting one to play around with.
build a mesh network of office chair sensors with premptive flatulaence alarming...
DIY oil prospecting here I come!