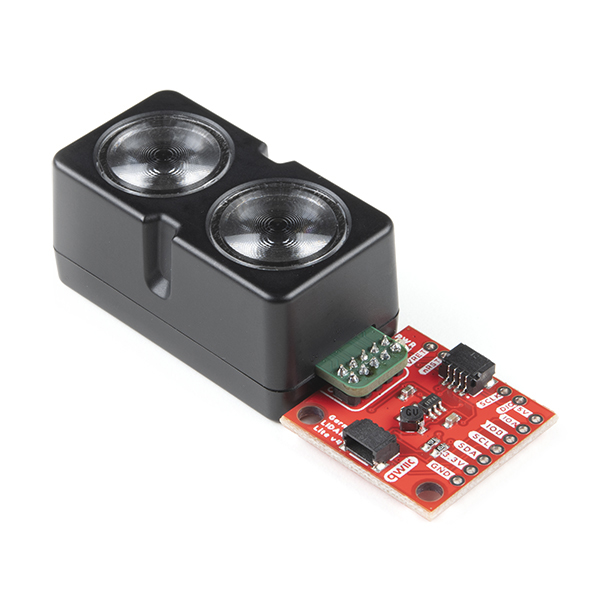
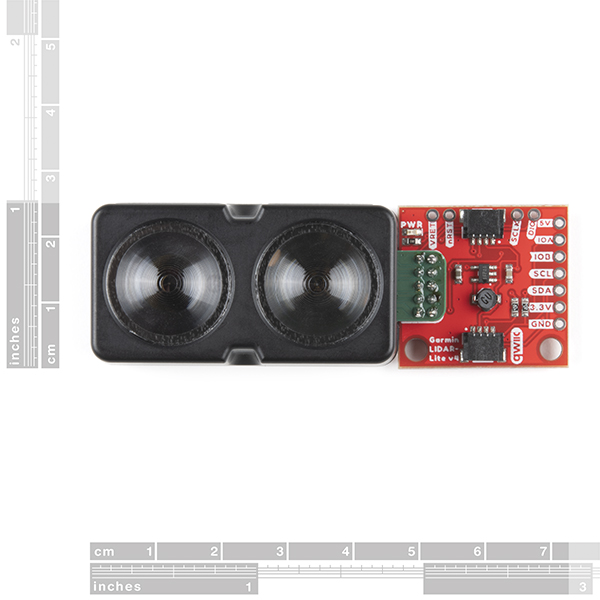
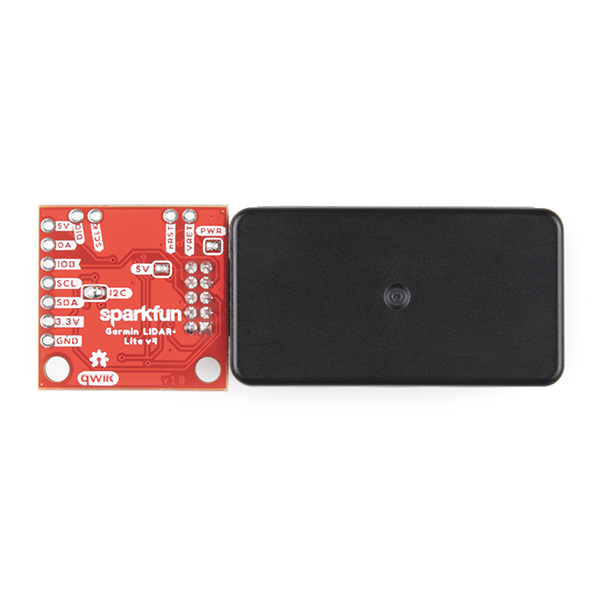
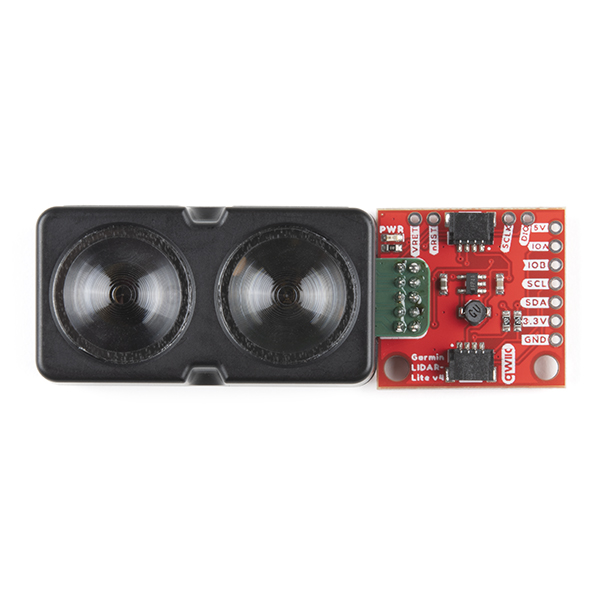
The LIDAR-Lite v4 Qwiic from GARMIN is a high-performance, wireless optical distance measurement sensor that doesn't require any soldering to get started. This is the ideal solution for drone, robot, IoT, or unmanned vehicle operations when space is tight and power is limited. This sensor has up to a 10 meter range, 1cm resolution, and requires 85mA during data acquisition. The user can read and write to the LIDAR-Lite v4 using the I2C protocol; this is where the addition of the SparkFun Qwiic system really shines. The LIDAR sensor requires 5V to operate but runs on 3V3 logic. With a 5V boost circuit and an easy-to-use Qwiic connector you can power the sensor and get distance measurements over Qwiic all with a single piece of hardware.
The LIDAR sensor works by sending out an infrared beam and measuring the time it takes to be reflected back. The LIDAR-Lite v4 utilizes LEDs rather than a laser for this iteration; therefore, it is inherently eye-safe under normal usage. The built-in nRF52840 microcontroller runs a pre-loaded "out of the box" stock application to calculate the distance between itself and something in front of it. The equipped nRF52840 also allows developers to create custom applications to expand on the "out of the box" functionality or connect to an external micro-controller running a custom user application.
The SparkFun LIDAR Lite v4 Arduino library makes getting data as easy as a call to the getDistance() function. The library also supports changing the I2C address of each LIDAR and provides an easy example of how to do so. Its low power-consumption and I2C address configuration means you can daisy-chain up to 10 of these sensors on one microcontroller platform.
Note: The I2C address of the Qwiic LIDAR-Lite v4 is 0x62 and is software-configurable to any address. A multiplexer/Mux is required to communicate to multiple Qwiic LIDAR-Lite v4 sensors on a single bus. If you need to use more than one Qwiic LIDAR-Lite v4 sensor consider using the Qwiic Mux Breakout.
The SparkFun Qwiic Connect System is an ecosystem of I2C sensors, actuators, shields and cables that make prototyping faster and less prone to error. All Qwiic-enabled boards use a common 1mm pitch, 4-pin JST connector. This reduces the amount of required PCB space, and polarized connections mean you can’t hook it up wrong.
- Resolution: 1cm
- Measurement repeatability:
- As measured indoors to a 90% reflective target
- 1cm is equivalent to one standard deviation
- Using “high accuracy” mode, with averaging:
- +/- 1cm to 2 meters
- +/- 2cm to 4 meters
- +/- 5cm to 10 meters
- Range: 5 cm to 10 meters (as measured from back of unit)
- Update rate:
- I2C = >200Hz typical
- ANT® = up to 200Hz to a 90% target indoors at 2m in normal operating mode
- Interface: I2C or ANT; user configurable for SPI using the Nordic SDK
- Power (operating voltage): 3.3VDC
- Operating temperature: -20 to 60° C
- LED wavelength: 940nm
- Beam divergence: 4.77°
- Optical aperture: 14.9mm
- Unit size (LxWxH): 2.8in x 1.0in x 0.9in
- Schematic
- Eagle Files
- Board Dimensions
- Hookup Guide
- Garmin LIDAR Lite v4 Product Information:
- SparkFun: Qwiic LIDAR Lite v4 Arduino library
- Qwiic Info Page
- GitHub Hardware Repo
Garmin LIDAR-Lite v4 LED - Distance Measurement Sensor (Qwiic) Product Help and Resources
Garmin LIDAR-Lite v4 (Qwiic) Hookup Guide
April 15, 2021
Connecting the Garmin LIDAR-Lite v4 to a microcontroller just got easier! Check out our hookup guide to get started.
Core Skill: Programming
If a board needs code or communicates somehow, you're going to need to know how to program or interface with it. The programming skill is all about communication and code.
Skill Level: Competent - The toolchain for programming is a bit more complex and will examples may not be explicitly provided for you. You will be required to have a fundamental knowledge of programming and be required to provide your own code. You may need to modify existing libraries or code to work with your specific hardware. Sensor and hardware interfaces will be SPI or I2C.
See all skill levels
Core Skill: Electrical Prototyping
If it requires power, you need to know how much, what all the pins do, and how to hook it up. You may need to reference datasheets, schematics, and know the ins and outs of electronics.
Skill Level: Rookie - You may be required to know a bit more about the component, such as orientation, or how to hook it up, in addition to power requirements. You will need to understand polarized components.
See all skill levels
Comments
Looking for answers to technical questions?
We welcome your comments and suggestions below. However, if you are looking for solutions to technical questions please see our Technical Assistance page.
Customer Reviews
No reviews yet.